Cowboys and Cowards
Growing up in the land of conquistadors and cowboys, my opportunities for IMC involved attacking thunderstorms or slipping into shallow ponds of fog. Neither was good for gaining instrument time or icing experience. My instructors and peers shared the same background.
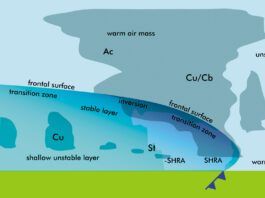
Intense Icing, Dude
Understanding the four different intensities of icing allows for better decision making and better PIREPS.
Think Like A Forecaster
From a weather perspective, what makes a flight a no-go? Sometimes its a simple glance at a stormy sky, an icing SIGMET, or winter weather warnings on the TV. But more often its the TAF that calls the shots. Whether its freezing rain, low ceilings, or a gusty crosswind, the buck stops with the TAF. That report comes straight from a highly qualified aviation forecaster at a local National Weather Service office and represents the best available predictions.
Readback: February 2015
I read with interest and obvious necessity for possible future application, your article on hypoxia, Get Your Mask On, in December, 2014.I fly a Malibu Mirage PA 46. Ive had several decompressions in the low 20s that were attributed to squat switch/pressure switch failures. Ive now added another immediate action to pressurization problems:
Winter Runways
The chief advantage of being instrument-rated is being able to travel in less-than-ideal weather. But, in winter, the triumph of a well-flown ILS to minimums in moderate snow can quickly turn to sheer terror after your smooth touchdown if you find yourself slipping off the side of an icy runway.Handling the aircraft is one thing; but, we must first understand what information is available about runway conditions, and how we can use that information to enhance our decision making and influence our technique.
When Low Fuel Becomes No Fuel
One of the most famous and tragic of fuel-exhaustion crashes occurred on Jan. 25, 1990. Upon arrival in the New York area after a flight from Bogot, the 707 was placed into a hold for an hour and 27 minutes due to fog at JFK. The pilots were not native English speakers and never used the actual word emergency in describing their fuel situation to ATC, using only minimum fuel instead and never stating their fuel state in minutes. During that time, they burned away all the fuel they needed to make Boston, their alternate.
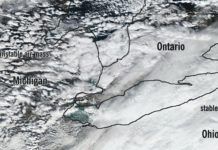
Turning Raw NEXRAD into Mosaic
Many pilots understand that the NEXRAD image they see on datalink weather doesnt exactly show where the rain is falling at that moment because of the delay in broadcasting the information up to the satellites and down to the weather receiver.
A Look Inside WSI Weather
Youve seen and almost certainly used a WSI Pilotbrief weather station in your travels. Its almost a required ritual of flight: Stop by the screen and make a last check of the radar or TFRs while you finish your lukewarm coffee. As a pilot, do you care whos behind the weather information you see at the FBO or in the cockpit? The answer is largely, No. But there are some differences between what you get from a briefer, on the web or from the competing XM weather provided by Baron Services. What we found more interesting was what a weather service must do in collecting, distilling and delivering the weather in a format on which pilots can depend.
Briefing: January 2010
Once upon a time it was considered just fine to polish frost smooth rather than scrape the junk off. Now the FAA has changed its mind. The rule is only binding on Parts 125, 135, or 91 subpart F (fractionals), but nine of the 12 frost-related accidents the FAA identified were with non-fractional Part 91 operations, so all of us might take note. Previous FAA guidance recommended removing all wing frost prior to takeoff, but allowed it to be polished smooth if the aircraft manufacturers recommended procedures were followed. But manufacturers never published standards for polished frost, and the FAA said it has no data to determine how to polish frost to satisfactory smoothness.
Flying High and Visual
The forecast said that deep, moist convection was likely for your afternoon flight. On your drive to the airport, you second-guess the 10,000-foot altitude you filed. Should you have filed for the low to mid teens? Perhaps you should have filed a much lower altitude to try and stay below the clouds?
Can I Log That?
Regulations are often vague, occasionally on purpose. What do you need to log instrument experience in an airplane? The rules state the tasks must be performed in actual weather conditions, or under simulated conditions using a view-limiting device. I get a kick out of the wording, when are you not flying in actual weather, whether VMC or IMC?
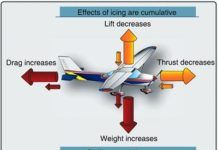
Ice and Tail Stalls
Every year structural icing claims a small but steady number of airplanes. Many of the accidents are on approach in clear air-after the airplane has already collected a load of ice. We look at it afterwards and wonder-the airplane had been doing fine-why did it crash well after it escaped from icing conditions?